Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Endocrine Research
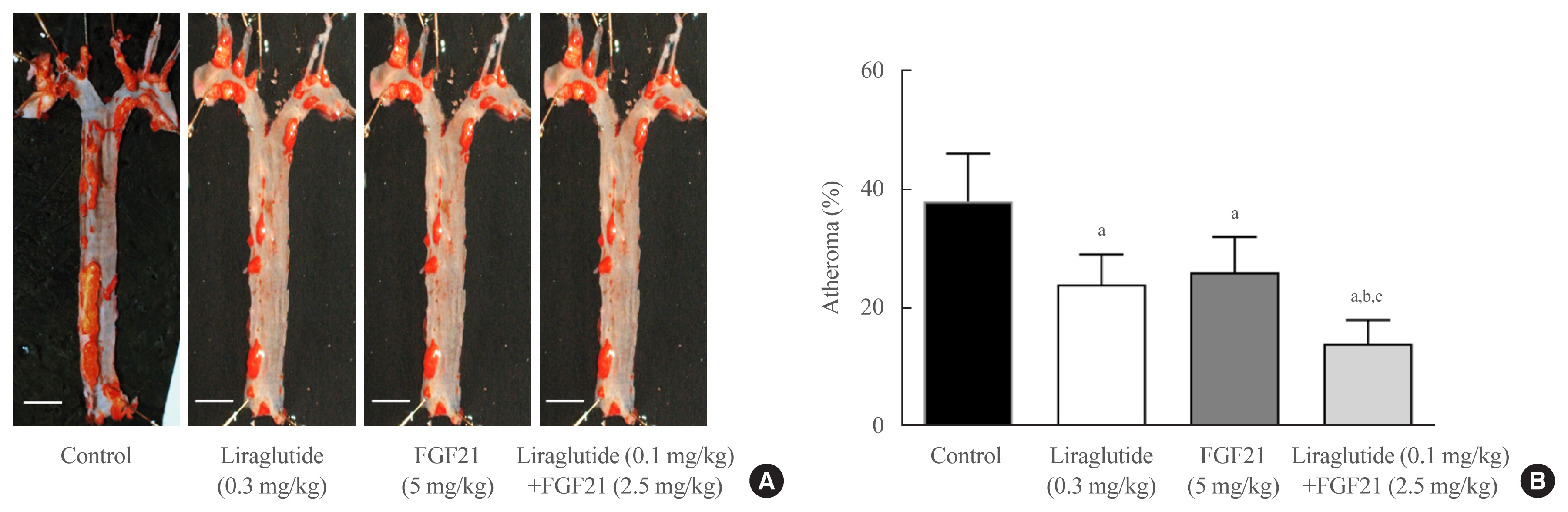
- Effects of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Analogue and Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Combination on the Atherosclerosis-Related Process in a Type 2 Diabetes Mouse Model
- Jin Hee Kim, Gha Young Lee, Hyo Jin Maeng, Hoyoun Kim, Jae Hyun Bae, Kyoung Min Kim, Soo Lim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):157-170. Published online February 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.781
- 6,891 View
- 176 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogues regulate glucose homeostasis and have anti-inflammatory properties, but cause gastrointestinal side effects. The fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) is a hormonal regulator of lipid and glucose metabolism that has poor pharmacokinetic properties, including a short half-life. To overcome these limitations, we investigated the effect of a low-dose combination of a GLP-1 analogue and FGF21 on atherosclerosis-related molecular pathways.
Methods
C57BL/6J mice were fed a high-fat diet for 30 weeks followed by an atherogenic diet for 10 weeks and were divided into four groups: control (saline), liraglutide (0.3 mg/kg/day), FGF21 (5 mg/kg/day), and low-dose combination treatment with liraglutide (0.1 mg/kg/day) and FGF21 (2.5 mg/kg/day) (n=6/group) for 6 weeks. The effects of each treatment on various atherogenesisrelated pathways were assessed.
Results
Liraglutide, FGF21, and their low-dose combination significantly reduced atheromatous plaque in aorta, decreased weight, glucose, and leptin levels, and increased adiponectin levels. The combination treatment upregulated the hepatic uncoupling protein-1 (UCP1) and Akt1 mRNAs compared with controls. Matric mentalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) were downregulated and phosphorylated Akt (p-Akt) and phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase (p-ERK) were upregulated in liver of the liraglutide-alone and combination-treatment groups. The combination therapy also significantly decreased the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Caspase-3 was increased, whereas MMP-9, ICAM-1, p-Akt, and p-ERK1/2 were downregulated in the liraglutide-alone and combination-treatment groups.
Conclusion
Administration of a low-dose GLP-1 analogue and FGF21 combination exerts beneficial effects on critical pathways related to atherosclerosis, suggesting the synergism of the two compounds. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Current status and future perspectives of FGF21 analogues in clinical trials
Zara Siu Wa Chui, Qing Shen, Aimin Xu
Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Design and pharmaceutical evaluation of bifunctional fusion protein of FGF21 and GLP-1 in the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
Xianlong Ye, Yingli Chen, Jianying Qi, Shenglong Zhu, Yuanyuan Wu, Jingjing Xiong, Fei Hu, Zhimou Guo, Xinmiao Liang
European Journal of Pharmacology.2023; 952: 175811. CrossRef - Use of FGF21 analogs for the treatment of metabolic disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Maria Paula Carbonetti, Fernanda Almeida-Oliveira, David Majerowicz
Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the potential mechanism of Simiao Yongan decoction in the treatment of diabetic peripheral vascular disease based on network pharmacology and molecular docking technology
Fang Cao, Yongkang Zhang, Yuan Zong, Xia Feng, Junlin Deng, Yuzhen Wang, Yemin Cao
Medicine.2023; 102(52): e36762. CrossRef - The Healing Capability of Clove Flower Extract (CFE) in Streptozotocin-Induced (STZ-Induced) Diabetic Rat Wounds Infected with Multidrug Resistant Bacteria
Rewaa Ali, Tarek Khamis, Gamal Enan, Gamal El-Didamony, Basel Sitohy, Gamal Abdel-Fattah
Molecules.2022; 27(7): 2270. CrossRef - Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) and Atherosclerosis: Explaining Their Pathophysiology, Association and the Role of Incretin-Based Drugs
Eleftheria Galatou, Elena Mourelatou, Sophia Hatziantoniou, Ioannis S. Vizirianakis
Antioxidants.2022; 11(6): 1060. CrossRef - Unlocking the Therapeutic Potential of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Analogue and Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Combination for the Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis in Type 2 Diabetes
Jang Won Son
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(1): 57. CrossRef - Effects of fasting on skeletal muscles and body fat of adult and old C57BL/6J mice
Mindaugas Kvedaras, Petras Minderis, Leonardo Cesanelli, Agne Cekanauskaite, Aivaras Ratkevicius
Experimental Gerontology.2021; 152: 111474. CrossRef - The Role of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 in Diabetic Cardiovascular Complications and Related Epigenetic Mechanisms
Mengjie Xiao, Yufeng Tang, Shudong Wang, Jie Wang, Jie Wang, Yuanfang Guo, Jingjing Zhang, Junlian Gu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Liraglutide Decreases Liver Fat Content and Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Levels in Newly Diagnosed Overweight Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Xinyue Li, Xiaojuan Wu, Yumei Jia, Jing Fu, Lin Zhang, Tao Jiang, Jia Liu, Guang Wang, Claudia Cardoso
Journal of Diabetes Research.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Differential importance of endothelial and hematopoietic cell GLP-1Rs for cardiometabolic versus hepatic actions of semaglutide
Brent A. McLean, Chi Kin Wong, Kiran Deep Kaur, Randy J. Seeley, Daniel J. Drucker
JCI Insight.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Current status and future perspectives of FGF21 analogues in clinical trials

- Standardization of Isolation Procedure and Analysis of Variables on Successful Isolation of Islet from the Human Pancreas.
- Song Cheol Kim, Duck Jong Han, Ik Hee Kim, Yoo Me We, Yang Hee Kim, Jin Hee Kim, Ji He Back, Dong Gyun Lim
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2006;21(1):22-31. Published online February 1, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2006.21.1.22
- 1,612 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Identifying the donor and isolation-related factors during the islet isolation would be greatly helpful to improve the result of human islet isolation for successful clinical islet transplantation. METHODS: Sixty-nine pancreata from cadaveric donors were isolated with standard protocol and analyzed to identify the donor factors and isolation variables for successful isolation. Islet isolations recovered > or = 100,000 Islet Equivalent (IEQ, n=53) were compared to islet mass less than 100,000 IEQ (n=16). RESULTS: The mean islet recovery was 216.0 x 10(3) +/- 173.7 x 10(3) (IEQ) before purification and 130.6 x 10(3) +/- 140.2 x 10(3) (IEQ) after purification. Mean purity was 54 +/- 31%. Mean age of donor was 31.2 +/- 13.2 year and mean cold ischemic time was 6.9 +/- 6.2 hour. Quality of isolated islets was acceptable in terms of bacterial culture, viability and secretory function in vitro and in vivo. In univariate analysis on successful isolation, status of pancreas was the only significant factor and sex, duration of collagenase expansion and digestion time were marginal factors. Stepwise multivariate logistic regression analysis showed donor sex, status of pancreas and digestion time were significant factors for the successful islet isolation. CONCLUSION: This study confirms some donor factors and variables in isolation process can influence the ability to obtain the successful isolation of human islet. Enough experiences and pertinent review of donor and isolation factors can make islet isolation successful, supporting the clinical islet transplantation without spending of cost.


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



